Division by Single Digits: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide for Students
Division by single digits is one of the most important foundational skills students learn in elementary and middle school math. Whether they are solving word problems, working with multi-digit numbers, or preparing for long division and algebra, mastering single-digit division provides the confidence and understanding students need for more advanced skills. Yet many learners struggle with division because they try to memorize procedures rather than understand the logic behind the process. This article breaks down division by single digits in a clear, visual, and student-friendly way to make the concept easier and more intuitive.
Division answers a simple question: how many equal groups can be made? When students learn how to divide step by step—especially using models, repeated subtraction, and place value—they become stronger problem solvers. Whether you're a teacher introducing division, a parent helping with homework, or a student learning independently, this guide offers a complete explanation of how to divide multi-digit numbers by a single digit, using examples, strategies, and tips that build deep understanding.
What Does Division by a Single Digit Mean?
Division by a single digit involves taking a larger number (the dividend) and splitting it into equal parts using a small number (the divisor). It helps students understand how numbers break apart and how multiplication and division are related.
Example: 48 ÷ 6
Here, 48 is being divided into 6 equal groups. How many items will each group have? This simple question leads students directly into understanding how division works.
Why Single-Digit Division Is Such a Crucial Skill
Mastering division by single digits prepares students for more complex operations, including:
- Long division
- Fractions and ratios
- Area and geometry concepts
- Algebraic reasoning
- Word problem solving
When students understand division conceptually—rather than memorizing steps—they can handle multi-digit problems with confidence and accuracy.
Strategies Students Should Learn for Dividing by Single Digits
There are several reliable strategies students can use when dividing by single digits. Each method strengthens number sense and helps students check their work.
1. Using Multiplication Facts
This is the fastest method once students know the multiplication table. To solve 42 ÷ 7, students simply find the multiplication fact that matches: 7 × 6 = 42, so the answer is 6.
2. Using Repeated Subtraction
Students subtract the divisor repeatedly until they reach zero. This builds a strong understanding of how division is related to subtraction.
42 ÷ 7 42 - 7 = 35 35 - 7 = 28 28 - 7 = 21 21 - 7 = 14 14 - 7 = 7 7 - 7 = 0 Number of subtractions = 6 Answer: 6
3. Using Place Value
When dividing larger numbers, students break them apart using hundreds, tens, and ones. This method is extremely useful in long division.
4. Using Area Models or Boxes
Students draw a model and break the dividend into manageable chunks. This reduces mistakes and makes division feel less intimidating.
5. Using Estimation to Check Answers
Students round numbers to quickly estimate and verify if their answer is reasonable.
Step-by-Step Guide: Dividing Larger Numbers by Single Digits
Let’s walk through several examples to show how division works in different situations.
Example 1: 84 ÷ 4
Step 1: Ask how many times 4 goes into the first digit. 8 ÷ 4 = 2
Step 2: Multiply and subtract to confirm: 2 × 4 = 8 8 - 8 = 0
Step 3: Bring down the next digit: 4 4 ÷ 4 = 1
Final answer: 21
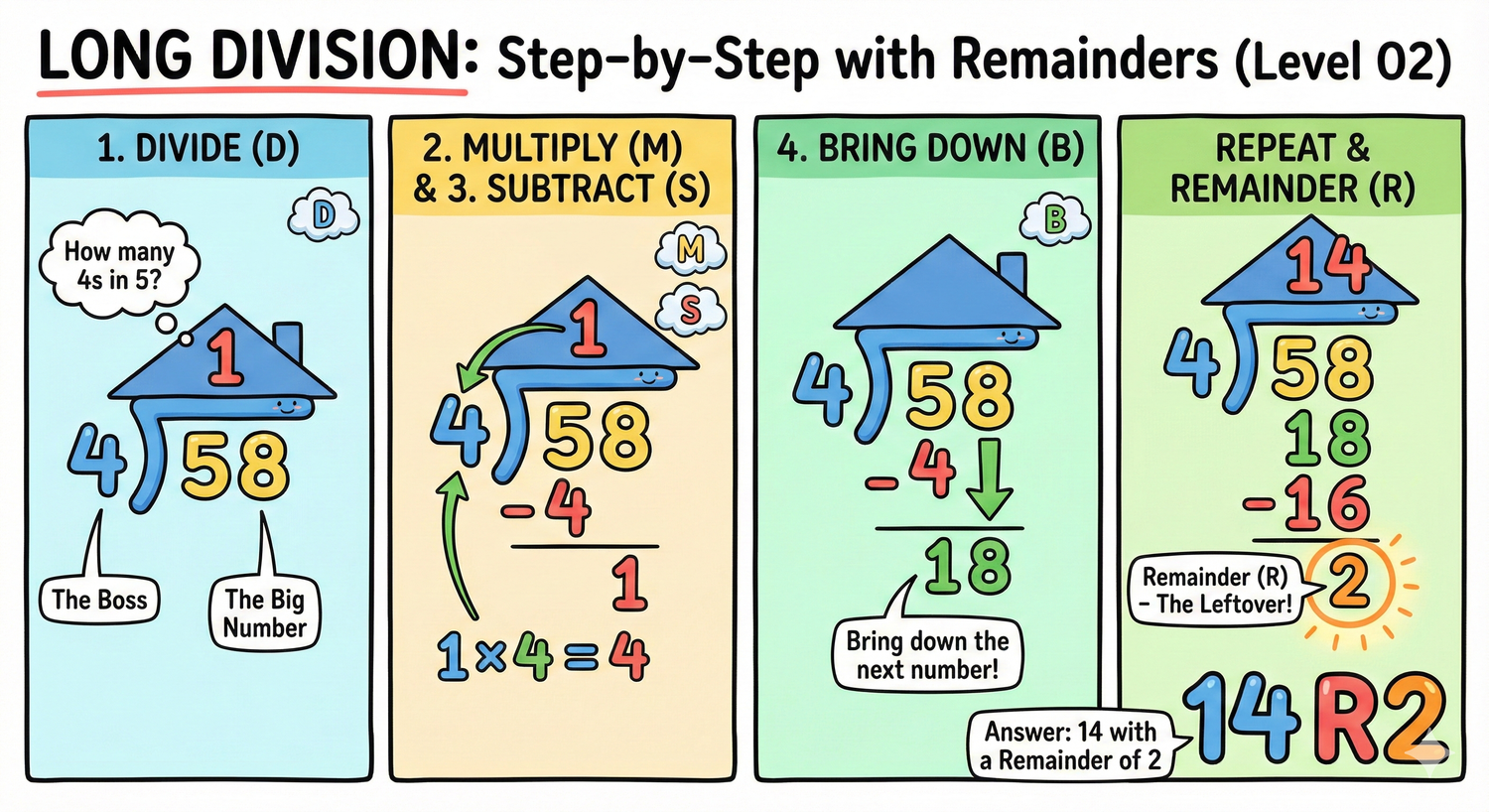
Example 2: 196 ÷ 7
Step 1: 19 ÷ 7 = 2 (since 2 × 7 = 14) Subtract 14 from 19 → remainder = 5
Step 2: Bring down 6 → forms 56 56 ÷ 7 = 8
Final answer: 28
Example 3: 502 ÷ 5
Step 1: 5 ÷ 5 = 1 → subtract → remainder 0
Step 2: Bring down 0 → 0 ÷ 5 = 0
Step 3: Bring down 2 → 2 ÷ 5 = 0 remainder 2
Final answer: 100 R2 (Students learn both quotient and remainder concepts.)
What to Do When There Is a Remainder
Not all division problems end perfectly. A remainder is what is left after dividing the dividend into equal groups. Students can represent remainders in different ways:
- As a whole number remainder (R2)
- As a fraction (2/5)
- As a decimal (0.4)
Example: 17 ÷ 5 = 3 R2 = 3 2/5 = 3.4 Understanding all three forms prepares students for higher grades.
Common Mistakes Students Make When Dividing by Single Digits
1. Forgetting Multiplication Facts
Students often struggle when they don’t know times tables. Daily practice improves speed and confidence.
2. Bringing Down Digits Incorrectly
This is common in long division. Clear steps and practice reduce these errors.
3. Misplacing Digits in the Quotient
Students sometimes place the answer in the wrong position, leading to an incorrect solution.
4. Not Subtracting Correctly
Incorrect subtraction causes bigger mistakes later in the problem.
5. Ignoring Remainders
Students may forget to include a remainder or misinterpret its meaning.
How to Help Students Master Division by Single Digits
- Practice multiplication daily. Division becomes much easier.
- Use visual models. Area models, blocks, or drawing groups help build understanding.
- Encourage estimation. Students should always check if their answer seems reasonable.
- Break numbers by place value. This reduces overwhelm.
- Use real-world examples. Sharing items or grouping objects helps the concept stick.
Final Thoughts: Division by Single Digits Builds Math Confidence
Dividing by single digits is a core skill every student needs before moving on to long division, fractions, and pre-algebra. When students understand the “why” behind division—through place value, multiplication facts, visual models, and step-by-step logic—they become more confident math learners. With consistent practice, students can solve division problems quickly, accurately, and with full comprehension. Whether learning in school or at home, mastering division by single digits lays the groundwork for success in every higher-level math topic.



Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.